前言 #
话说一直想找时间写写关于学图形学时学到的东西,但又觉得码字好累(图形学中挺多公式和推导),这里先简单介绍一下如何使用 C/C++/Python 等语言画分形吧,其余的改天再补充。
数学家们对分形的研究也有很长时间了,著名的 Mandelbrot set、Julia set、Newton’s fractal 等,嘛,水平有限,只能从程序方面欣赏她的美了。
一些关于分形的网站: http://hpdz.net/
Mandelbrot set #
C/C++:
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
using std::complex;
uint8_t mandelbrot(complex<double> z, int max_iter)
{
complex<double> c = z;
for (int k = 0; k < max_iter; k++)
{
if (std::abs(z) > 2.) return k;
z = std::pow(z, 2.) + c;
}
return max_iter;
}
int main()
{
int w = 500, h = 500;
double zoom_lx = -2., zoom_rx = 1.,
zoom_ly = -1.5, zoom_ry = 1.5;
int max_iter = 1000;
FILE* fp = fopen("mandelbrot_frac_cpp.ppm", "wb");
fprintf(fp, "P6 %d %d 255 ", w, h);
for (int i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
double zy = zoom_ly + (double(i) / double(h - 1)) * (zoom_ry - zoom_ly);
for (int j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
double zx = zoom_lx + (double(j) / double(w - 1)) * (zoom_rx - zoom_lx);
complex<double> z(zx, zy);
uint8_t n = mandelbrot(z, max_iter);
double r = (108 * n) % 256,
g = (88 * n) % 256,
b = (245 * n) % 256;
fprintf(fp, "%c%c%c", uint8_t(r), uint8_t(g), uint8_t(b));
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
该代码会在执行文件同目录下生成一个 mandelbrot_frac_cpp.ppm 文件,linux系统可直接打开,windows系统上可使用一些转换工具,或者使用如下 python 脚本:
from PIL import Image
import sys
im = Image.open(sys.argv[1])
im.show()
im.save(open(sys.argv[2], 'wb'))
将上面脚本保存为 ppm2png.py 文件,然后命令行中运行:
py ppm2png.py mandelbrot_frac_cpp.ppm mandelbrot_frac_cpp.png
即可看到 png 格式的分形图像:
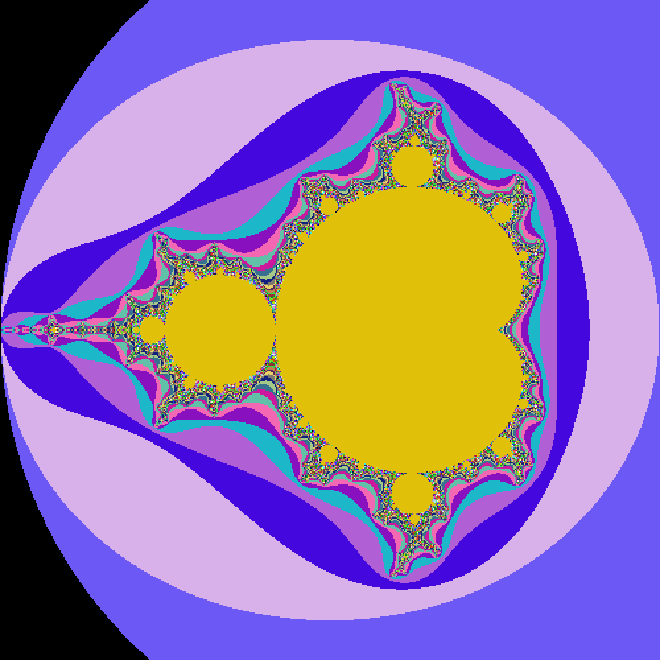
实际上我还没研究明白如何才能等比例无限放大 mandelbrot 分形的局部。
Python:
import numpy as np
import cv2 as cv
xa = -2.0
xb = 1.0
ya = -1.5
yb = 1.5
maxIt = 1000
imgx = 1200
imgy = 1200
image = np.zeros((imgx, imgy, 3), np.uint8)
for y in range(imgy):
zy = y * (yb - ya) / (imgy - 1) + ya
for x in range(imgx):
zx = x * (xb - xa) / (imgx - 1) + xa
z = zx + zy * 1j
c = z
i = 0
while i < maxIt:
if abs(z) > 2.0: break
z = z * z + c
i += 1
r = i * 128 % 256
g = i * 2 % 256
b = i * 2 % 256
image[y, x] = [int(b), int(g), int(r)]
cv.imwrite('mandelbort_frac_py.png', image)
该代码将输出一个 mandelbrot_frac_py.png 文件:
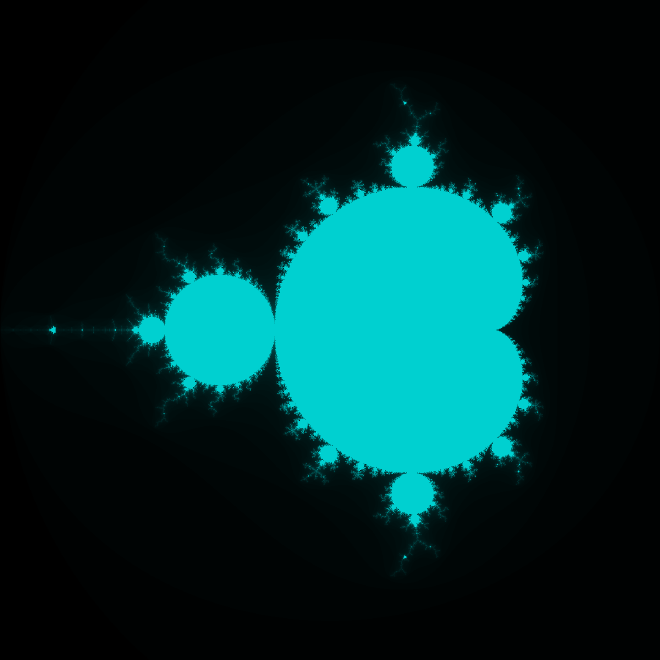
Newton fractal #
这是一篇介绍牛顿迭代法的分形文章: https://www.chiark.greenend.org.uk/~sgtatham/newton/
这里画一个使用牛顿迭代 \( z = z^5 - 1 \) 的 \(5\) 个根所产生的分形图像。
C/C++:
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
class Vec3b {
public:
Vec3b(uint8_t r, uint8_t g, uint8_t b) : e{r, g, b} {}
uint8_t r() { return e[0]; }
uint8_t g() { return e[1]; }
uint8_t b() { return e[2]; }
uint8_t operator[](size_t i) { return e[i]; }
uint8_t e[3];
}
auto fz = [](complex<double> z) { return std::pow(z, 5.) - complex<double>(1., 0.); };
auto dz = [](complex<double> z) { return 5. * std::pow(z, 4.); };
Vec3b fractal(size_t max_it, complex<double> z, complex<double> roots[], Vec3b color[])
{
double a = -0.5;
for (size_t k = 0; k < max_it; k++)
{
z -= fz(z) / dz(z);
for (size_t r = 0; r < 5; r++)
{
complex<double> distance = z - roots[r];
if (std::abs(distance) < 1e-6)
return Vec3b(
(color[r][0] * k) % 256,
(color[r][1] * k) % 256,
(color[r][2] * k) % 256);
}
}
return color[5];
}
int main()
{
size_t w = 500, h = 500;
FILE* fp = fopen("picture.ppm", "wb");
fprintf(fp, "P6 %d %d 255 ", w, h);
complex<double> roots[5] = {
complex<double>(1, 0),
complex<double>(-(std::sqrt(5) + 1) / 4., -std::sqrt((5 - std::sqrt(5)) / 8.)),
complex<double>((std::sqrt(5) - 1) / 4., std::sqrt((5 + std::sqrt(5)) / 8.)),
complex<double>((std::sqrt(5) - 1) / 4., -std::sqrt((5 + std::sqrt(5)) / 8.)),
complex<double>(-(1. + std::sqrt(5)) / 4., std::sqrt((5 - std::sqrt(5)) / 8.)),
};
Vec3b color[6] = {
Vec3b(130, 18, 245),
Vec3b(44, 245, 18),
Vec3b(254, 183, 18),
Vec3b(245, 14, 160),
Vec3b(14, 121, 245),
Vec3b(0, 0, 0)
};
for (size_t i = 0; i < h; i++)
{
double zy = 10. * (double(i) / double(h - 1)) - 5.;
for (size_t j = 0; j < w; j++)
{
double zx = 10. * (double(j) / double(w - 1)) - 5.;
complex<double> z(zx, zy);
Vec3b c = fractal(100, z, roots, color);
fprintf(fp, "%c%c%c", c.r(), c.g(), c.b());
}
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
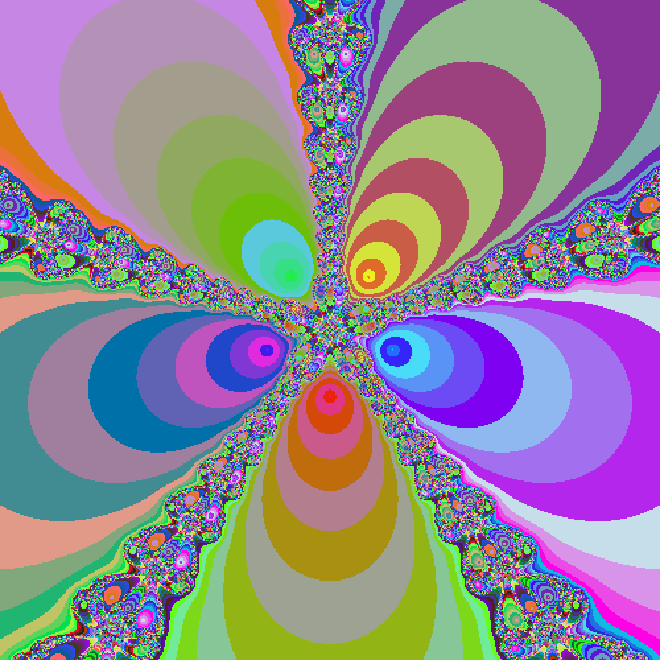
该代码将输出如下图像结果:


