Tarjan算法可以用来求有向图的强连通分量个数。算法由Robert Tarjan于1972年发明的。
算法分析 #
Tarjan算法的主要算法部分也是 dfs,但利用了重要的额外信息。下面详细分析了算法的执行过程。
强连通子图的重要特点:对于强连通子图,有一个特定的事实就是,该子图一定形成环,那么从该子图中任意点出发,总能回到出发点。
基于上面这一点,Tarjan算法通过维护两个存放顶点访问顺序(时间)的数组。如果子图形成环,则将处于环中的每一个顶点的访问顺序置为该环的出发点的访问时间,以表明他们是一个强连通子图。可能你会怀疑进入环后,不会只在环中遍历,可能会跳到其他顶点上。实际上这担心是多余,因为图结构使用邻接链表表示,强连通子图使用dfs进行遍历时,只会寻找与当前顶点连接的出度顶点,而形成环的子图中,会很合理的按顺序遍历完。对于孤立点,则自身就是一个环,即强连通分量。
这就是Tarjan算法的思想 —— 维护两个存储访问顺序的数组,然后将形成环的节点的访问时间都置为该强连通子图的出发点的访问时间。
通过下图可以更直观的理解Tarjan算法的执行过程(图来自维基):
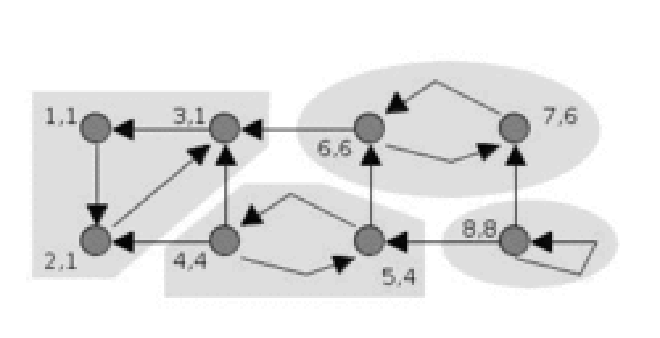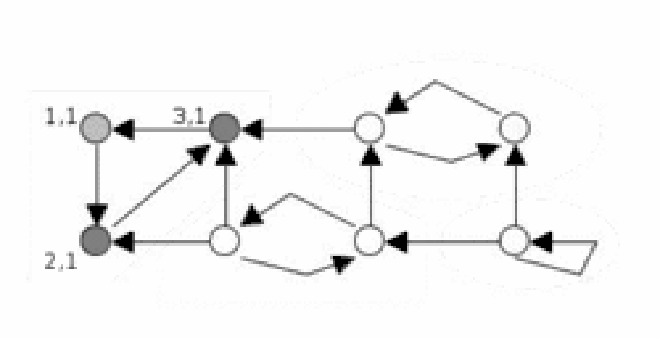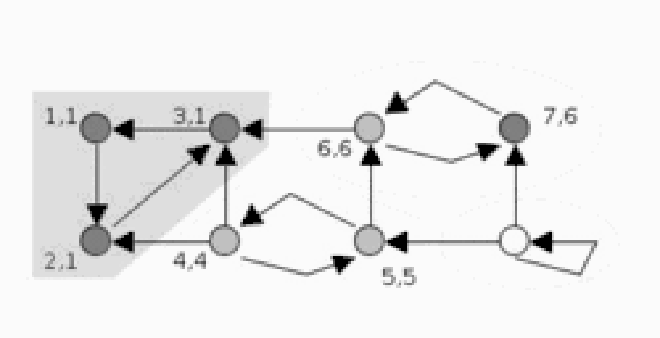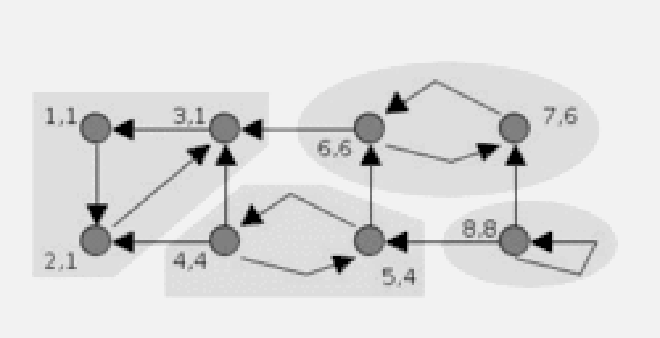
时间复杂度 #
最坏情况是图G的强连通子图就是其本身(这样的图称为强连通图),这时 dfs 的消费为 \( O(|V| + |E|) \),最后一次 dfs 的while循环再消费掉 \( O(V) \),所以 dfs() 最坏情况为 \( O(|V| + |E|) \)。最后 tarjan() 的总消耗为 \( O (V^2) \)。
空间复杂度 #
显然为 \( O(V) \)。
算法实现 #
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <stack>
#include <list>
#include <minmax.h>
using namespace std;
const int N = 10010;
list<int> *adj;
stack<int> s;
int vis[N], low[N];
bool onstack[N];
int times = 0, scc = 0;
void addEdge(int u, int v)
{
adj[u].push_back(v);
}
void dfs(int u)
{
vis[u] = low[u] = times++;
s.push(u);
onstack[u] = true;
for (list<int>::iterator i = adj[u].begin(); i != adj[u].end(); ++i)
{
int v = *i;
if (vis[v] == -1)
{
dfs(v);
low[u] = min(low[u], low[v]);
}
else if (onstack[v] == true)
low[u] = min(low[u], vis[v]);
}
if (low[u] == vis[u])
{
while (s.top() != u)
{
int w = s.top();
cout << w << ' ';
onstack[w] = false;
s.pop();
}
int w = s.top();
cout << w << endl;
onstack[w] = false;
s.pop();
scc++;
}
}
void tarjan(int V, int E)
{
adj = new list<int>[V + 1];
list<int> v;
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++)
{
vis[i] = low[i] = -1;
onstack[i] = false;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= E; i++)
{
int u, w;
cin >> u >> w;
adj[u].push_back(w);
}
for (int i = 1; i <= V; i++)
if (vis[i] == -1)
dfs(i);
cout << "该图的强连通分量个数为:" << scc << endl;
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int V, E;
cin >> V >> E;
tarjan(V, E);
return 0;
}
代码中 dfs() 函数的 for 循环后面的部分用来输出所有强连通子图中的顶点,并求出强连通分量个数。
下面以前面wiki图为例测试一下算法。
算法测试结果:
3 2 1
7 6
5 4
8
该图的强连通分量个数为:4

